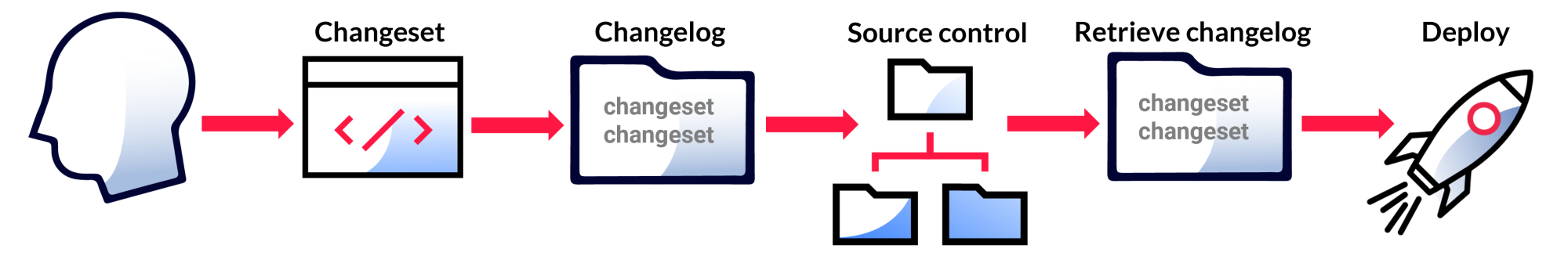
Changeset
A changeset is the basic unit of change in Liquibase. You store all your changesets in your Changelog. Your changesets contain Change Types that specify what each change does, like creating a new table or adding a column to an existing table.
A changeset is uniquely tagged by both the author and id attributes (author:id), as well as the changelog file path. The id tag is just an identifier—it doesn't direct the order that changes are run and doesn't have to be an integer. To deploy the changeset with the update command, you must include both author and id. You can specify Preconditions, Contexts, Labels, and other attributes in individual changesets to control exactly when they run.
It is a best practice to specify only one type of change per changeset. Doing so avoids failed auto-commit statements that can leave the database in an unexpected state. When you deploy your changes, each changeset either succeeds or fails; if it fails, you can correct it and deploy again. You can also add comments to individual changesets to explain why they're important.
By default, Liquibase runs changesets as a single transaction. You can modify this behavior with the runInTransaction attribute. Once you run a changeset, Liquibase does not re-run it unless you specify runAlways or runOnChange for that changeset.
File formats
The format of your changeset depends on the file type of your changelog, which can be SQL, XML, YAML, or JSON. For examples of entire changelogs in each format, see the pages linked in the following drop-down tabs.
Read more: Example Changelogs: SQL Format.
--changeset nvoxland:1
create table company (
id int primary key,
address varchar(255)
);Read more: Example Changelogs: XML Format.
<changeSet id="1" author="nvoxland">
<createTable tableName="company">
<column name="address" type="varchar(255)"/>
</createTable>
</changeSet>Read more: Example Changelogs: YAML Format.
databaseChangeLog:
- changeSet:
id: 1
author: nvoxland
changes:
- createTable:
tableName: company
columns:
- column:
name: addressRead more: Example Changelogs: JSON Format.
{
"changeSet": {
"id": "1",
"author": "nvoxland",
"changes": [
{
"createTable": {
"tableName": "company",
"columns": [
{
"column": {
"name": "address"
}
}
]
}
}
]
}
}For other formats, see Example Changelogs: Other Formats.
Runtime logic
When you run a database update, Liquibase reads the changesets in your changelog in order. For each one, it checks the DATABASECHANGELOG table to see if the combination of id/author/filepath has already been deployed.
If a changeset has already been deployed to your database, Liquibase skips it unless it has a runAlways=true tag. After running all the changes in the changesets, Liquibase inserts a new row with the id/author/filepath along with an MD5Sum (checksum) of the changeset in the DATABASECHANGELOG table. For more information, see Changeset Checksums.
Note: filepath is the path that defines the changelog-file attribute. Even if the same file is referenced with a different path, that is considered a different file unless the logicalFilePath is defined.
Liquibase attempts to execute each changeset in a transaction that is committed at the end, or rolled back if there is an error. Some databases auto-commit statements, which interferes with this transaction setup and could lead to an unexpected database state. Therefore, it is best practice to have just one change per changeset unless there is a group of non-auto-committing changes that you want to apply as a transaction such as inserting data.
Attributes
You can apply these attributes to individual changesets:
| Attribute | Description | Requirement |
|---|---|---|
author
|
Specifies the creator of the changeset. Must be non-empty if the global argument strict is true. Can be empty only if strict is false. |
Required |
id
|
Specifies an alpha-numeric identifier. Note: If there are zeros in the id, it is best practice to put quotes around the id, such as "1.10". This allows all characters to be retained. |
Required |
context
|
Specifies the changeset contexts to match. Contexts are tags you can add to changesets to control which changesets will be executed in any particular migration run. |
Optional |
created
|
Stores dates, versions, or any other string of value without using remarks (comments) attributes. Since 3.5 | Optional |
dbms
|
Specifies which database type |
Optional |
failOnError
|
Defines whether a database migration will fail if an error occurs while executing the changeset. Default: |
Optional |
ignore
|
Tells Liquibase to treat a particular changeset as if it does not exist. Default: |
Optional |
labels
|
Specifies the changeset labels to match. Labels are tags you can add to changesets to control which changesets will be executed in any migration run. |
Optional |
logicalFilePath
|
Overrides the file name and path when creating the unique identifier of changesets. It is required when you want to move or rename changelogs. |
Optional |
objectQuotingStrategy
|
Controls how object names are quoted in the SQL files generated by Liquibase and used in calls to the database. Default:
Not supported with Formatted Mongo. |
Optional |
onValidationFail
|
Controls what Liquibase does when a changeset fails validation. Values are HALT and MARK_RAN. Default: HALT. |
Optional |
runAlways
|
Executes the changeset on every run, even if it has been run before. Default: |
Optional |
runInTransaction
|
Specifies whether the changeset can be run as a single transaction (if possible). Default: Warning: If |
Optional |
runOnChange
|
Executes the changeset when you create it and each time it changes. Default: |
Optional |
runOrder
|
Specifies whether a changeset should be run before or after all other changesets instead of running it sequentially based on its order in the changelog. Valid values are first and last. It is typically used when you want a changeset to be always executed after everything else but don’t want to keep moving it to the end of the changelog. Setting the runOrder to last will automatically move the changeset to the final place in the changeset run order. Since 3.5Note: |
Optional |
runWith
|
Specifies a native executor to run your SQL ( |
Optional |
runWithSpoolFile
|
Specifies a spool file to send output to when you deploy a particular changeset. |
Optional |
Sub-tags
You can nest these tags within a changeset, at the same level as the Change Type:
| Tag | Description |
|---|---|
comment
|
Specifies the description of the changeset. XML comments provide the same benefit. |
preConditions
|
Preconditions required to execute the changelog. If global, must be passed before the changeset is run. Preconditions are typically used for doing a data sanity check before doing something unrecoverable such as a Not supported with Formatted Mongo. |
rollback
|
Specifies SQL statements or Change Type tags that describe how to rollback the changeset. For more information, see Liquibase Rollback Workflow and Automatic and Custom Rollbacks. |
rollbackSqlFile
|
Liquibase Pro 4.26.0+. Formatted SQL only. Lets you specify a SQL file to roll back rather than an inline SQL statement. For more information, see Example Changelogs: SQL Format. |
validCheckSum
|
Adds a checksum that is considered valid for this changeset, regardless of what is stored in the database. It is
primarily used when you need to change a changeset and don't want errors thrown on databases on which it has already been run (not a recommended procedure). Special value "1:any" will match to any checksum and will not execute the changeset on ANY change. Since 1.7 |
| <Any Refactoring Tag(s)> | Specifies the database change(s) to run as part of the changeset (Change Types). |
Some Change Types support additional nested tags, like column, where, and whereParams. The scope of these tags is limited to the Change Type you place them in.
