Create an AWS Task definition to run Liquibase commands
Last updated: September 2, 2025
There are multiple ways to operate Liquibase container within AWS. The example provided is specific to containers in ECS, and is one of several solutions. A task definition is a JSON text file that outlines how your containers operate in ECS. In the context of Liquibase, you write task definitions to run Liquibase commands on AWS. Follow the guide below to learn how to create Liquibase specific task definitions.
Before you begin
Create an S3 bucket or a GitHub repository to store configuration files
If you are using S3, create an IAM user with access to the S3 bucket, and generate security credentials for the same user.
Required additional AWS Resources:
MySQL RDS Instance - If you are using MySQL DB
AWS Fargate ECS cluster
IAM role to access the CloudWatch Logs, create Task Definitions, etc.
Procedure
Create a task definition for Liquibase commands in AWS Fargate
Navigate to your Amazon Elastic Container Service console.
Select Task definitions from the left side navigation.
Click the Create a new task definition button
Use this example task definition below to build a new task by replacing the placeholder values of <PRO CONTAINER IMAGE LINK> and <S3 BUCKET NAME> with your values.
In this example, task definitions are arranged as individual Liquibase commands. You can create batch task definitions that contain multiple Liquibase commands by following AWS best practices.
Task definition example
{
"taskDefinitionArn": "arn:aws:ecs:us-east-1:{account_number}:task-definition/connect-command",
"containerDefinitions": [
{
"name": "Liquibase-Pro",
"image": "<PRO CONTAINER IMAGE LINK>",
"cpu": 0,
"portMappings": [],
"essential": true,
"command": [
"--defaults-file=s3://<s3 BUCKET NAME>/liquibase.properties",
"connect"
],
"environment": [],
"mountPoints": [],
"volumesFrom": [],
"logConfiguration": {
"logDriver": "awslogs",
"options": {
"awslogs-group": "/ecs/connect-command",
"awslogs-create-group": "true",
"awslogs-region": "us-east-1",
"awslogs-stream-prefix": "ecs"
}
},
"systemControls": []
}
],
"family": "connect-command",
"taskRoleArn": "arn:aws:iam::{account_number}:role/ecsTaskExecutionRole",
"executionRoleArn": "arn:aws:iam::{account_number}:role/ecsTaskExecutionRole",
"networkMode": "awsvpc",
"revision": 1,
"volumes": [],
"status": "ACTIVE",
"requiresAttributes": [
{
"name": "com.amazonaws.ecs.capability.logging-driver.awslogs"
},
{
"name": "ecs.capability.execution-role-awslogs"
},
{
"name": "com.amazonaws.ecs.capability.ecr-auth"
},
{
"name": "com.amazonaws.ecs.capability.docker-remote-api.1.19"
},
{
"name": "com.amazonaws.ecs.capability.task-iam-role"
},
{
"name": "ecs.capability.execution-role-ecr-pull"
},
{
"name": "com.amazonaws.ecs.capability.docker-remote-api.1.18"
},
{
"name": "ecs.capability.task-eni"
},
{
"name": "com.amazonaws.ecs.capability.docker-remote-api.1.29"
}
],
"placementConstraints": [],
"compatibilities": [
"EC2",
"FARGATE"
],
"requiresCompatibilities": [
"FARGATE"
],
"cpu": "1024",
"memory": "3072",
"runtimePlatform": {
"cpuArchitecture": "ARM64",
"operatingSystemFamily": "LINUX"
},
"registeredAt": "2024-10-29T15:37:24.193Z",
"registeredBy": "arn:aws:sts::{account_number}:assumed-role/AWSReservedSSO_MarketplaceLimitedPermissions_1c0e25eeb793d12a/{username}",
"enableFaultInjection": false,
"tags": []
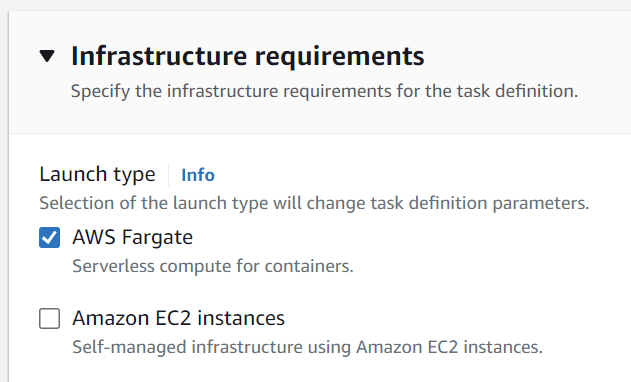
}Ensure that the Launch type selected is AWS Fargate.
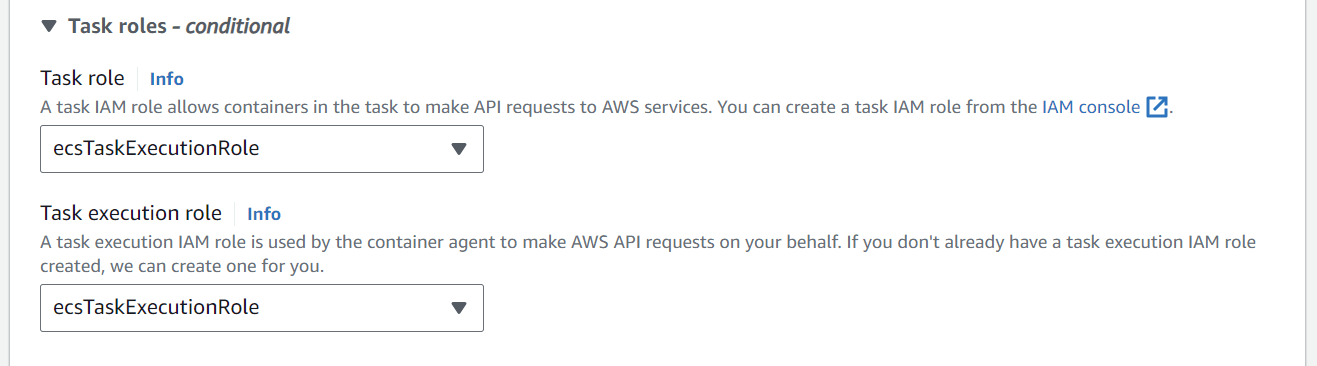
Set both the Task role and execution role to ecsTaskExecutionRole. This role is created by default when we create a ECS Fargate cluster.
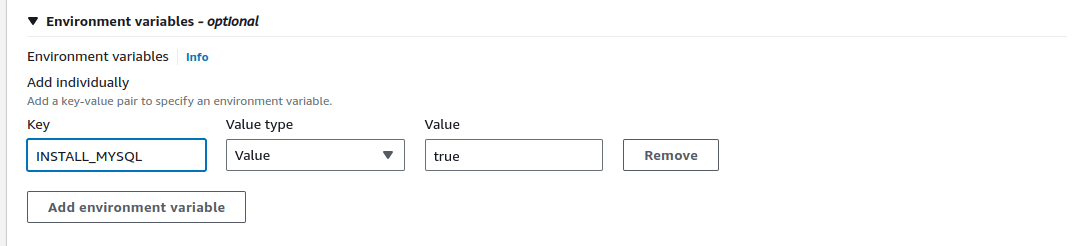
This is the container you may want to extend the Docker container to use SQL, mySQL, NoSQL, or any other type of extension.
Ensure that Container has this Image URI: 709825985650.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/liquibase/liquibase/liquibase-pro:<insert_image_tag>
Create an AWS Task Definition to Run Liquibase Commands