What is a Changeset?
Last updated: September 2, 2025
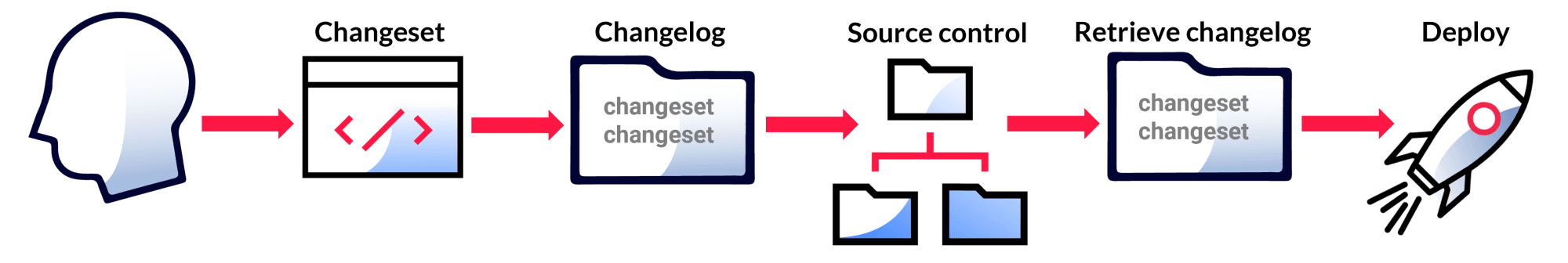
A changeset is the basic unit of change in Liquibase. You store all your changesets in your Changelog. Your changesets contain Change Types that specify what each change does, like creating a new table or adding a column to an existing table.
A changeset is uniquely tagged by both the author and id attributes (author:id), as well as the changelog file path. The id tag is just an identifier—it doesn't direct the order that changes are run and doesn't have to be an integer. To deploy the changeset with the update command, you must include both author and id. You can specify Preconditions, Contexts, Labels, and other attributes in individual changesets to control exactly when they run.
It is a best practice to specify only one type of change per changeset. Doing so avoids failed auto-commit statements that can leave the database in an unexpected state. When you deploy your changes, each changeset either succeeds or fails; if it fails, you can correct it and deploy again. You can also add comments to individual changesets to explain why they're important.
By default, Liquibase runs changesets as a single transaction. You can modify this behavior with the runInTransaction attribute. Once you run a changeset, Liquibase does not re-run it unless you specify runAlways or runOnChange for that changeset.
What is a changeset?
Liquibase source control workflow
File formats
The format of your changeset depends on the file type of your changelog, which can be SQL, XML, YAML, or JSON. See the pages linked in the following drop-down tabs for examples of entire changelogs in each format.
Changeset examples
--liquibase formatted sql
--precondition-name precondition-attribute:value
--changeset author:id
changetype name (
changetype attributes
);
--rollback <SQL statement>
--rollbackSqlFile path:<filepath>
runOnChange changeset attribute
<changeSet author="your.name" id="changeset01" runOnChange="true" >
<createProcedure>
. . .
</createProcedure>
</changeSet>